Press-room / news / Science news /
Redox differences between neurons and astrocytes in vivo in ischemic brain tissues of rodents
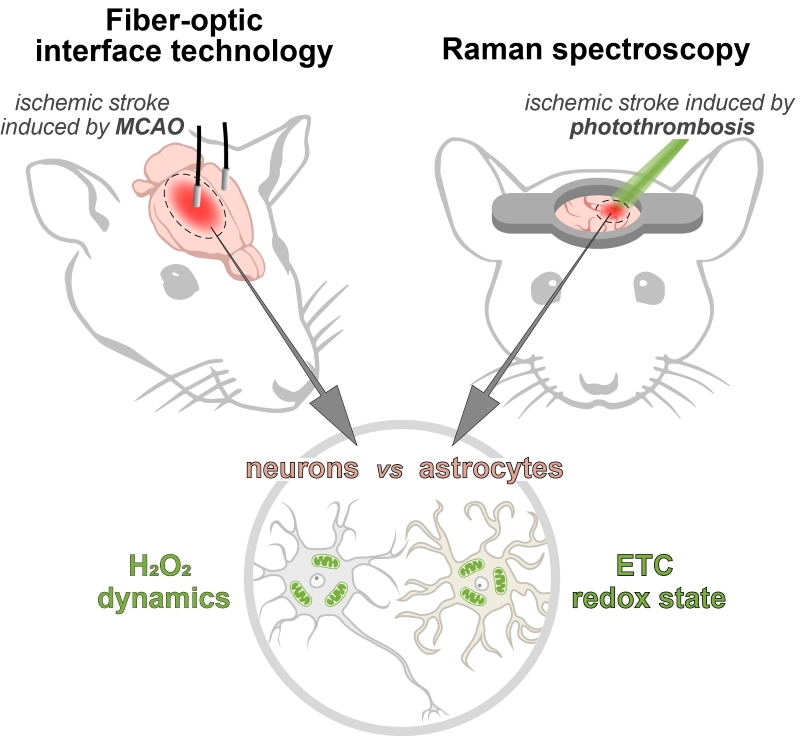
Combinations of novel in vivo approaches allow to detail redox events with high spatiotemporal resolution in the brain tissues of laboratory animals. We demonstrated redox differences between neurons and astrocytes in damaged brain areas of rodents in vivo during ischemic stroke in model of middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats and photothrombosis model in mice. Using highly sensitive genetically encoded biosensor HyPer7 and a fiber-optic neurointerface technology, we demonstrated that astrocytes differ from neurons in elevated hydrogen peroxide levels in the ischemic brain area of rats. Raman microspectroscopy also revealed the overloading of the mitochondrial electron transport chain precisely in astrocytes in the brain tissues of awake mice during acute ischemia. The results are published in Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.
may 21, 2025


