Press-room / news / Science news /
Redox differences between neonatal and adult cardiomyocytes under hypoxia
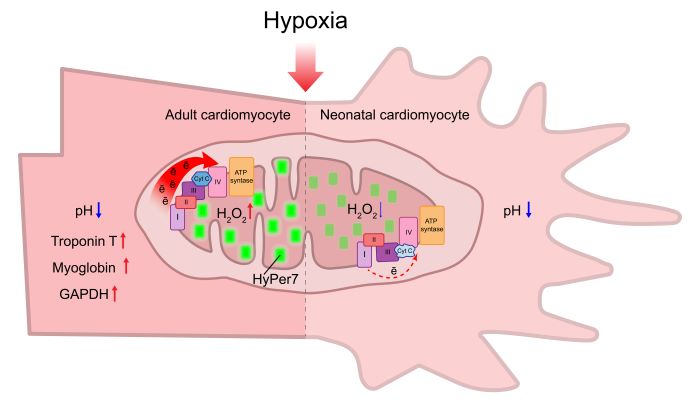
It is a known fact that oxidative stress plays a key role in the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease. However, why do neonatal cardiomyocytes exhibit greater resistance to hypoxia compared to adult cell types?
A team of scientists from the IBCh RAS, Lomonosov Moscow State University and other Russian institutes studied the differences in the redox state of neonatal and adult rat cardiomyocytes under hypoxic conditions. Using the highly sensitive HyPer7 biosensor, authors found that hypoxia causes an increase in H2O2 production in adult cardiomyocytes, while neonatal cells, on the contrary, experience a decrease in basal H2O2 levels under the same conditions. This finding correlates with other data obtained by the authors using Raman microspectroscopy, which demonstrate a marked difference in the properties of the mitochondrial electron transport chain of adult and neonatal cells. In particular, in adult cardiomyocytes, hypoxia causes the significant increase in the respiratory chain loading with electrons, while in neonatal cells this effect is not observed. The work was published in Free Radical Biology and Medicine journal.
december 4, 2023


